SCIENCE Epigenomic
Controllers
Our programmable mRNA medicines called epigenomic controllers leverage nature’s innate mechanism for gene regulation and epigenetically tune dysregulated genes back to normal levels of expression.
What Are Epigenomic Controllers?
Epigenomic controllers are mRNA-based therapeutics that are programmed to target unique sequences within the genome with high specificity to controllably tune gene expression for a tailored duration, allowing for options beyond just “all on” or “all off.” By acting pre-transcriptionally at the highest level of gene regulation, our controllers are designed to overcome the compensatory autoregulation often associated with key disease drivers, including those historically undruggable with conventional approaches.
How Do Epigenomic Controllers Work?
Our initial programs leverage lipid-nanoparticle (LNP) technology. When delivered as LNPs, epigenomic controllers are taken up by cells where the mRNA cargo is translated into therapeutic protein by the cell’s natural machinery.
The mRNA expresses a fusion protein comprised of a highly specific DNA-binding domain and an epigenomic effector capable of controlling the various regulators of gene expression by leveraging a broad set of epigenetic mechanisms, such as DNA methylation/demethylation and those controlling the state of chromatin (e.g., histone modification, acetylation, etc.).
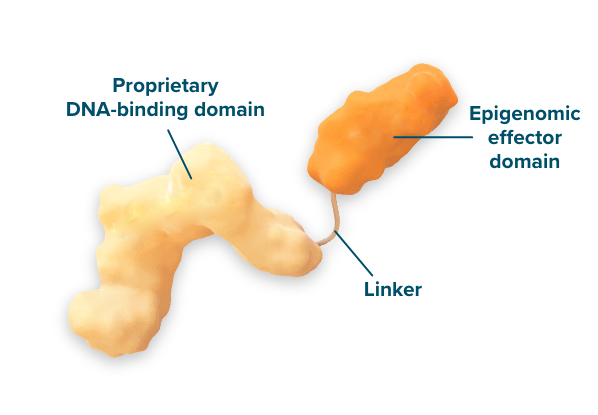
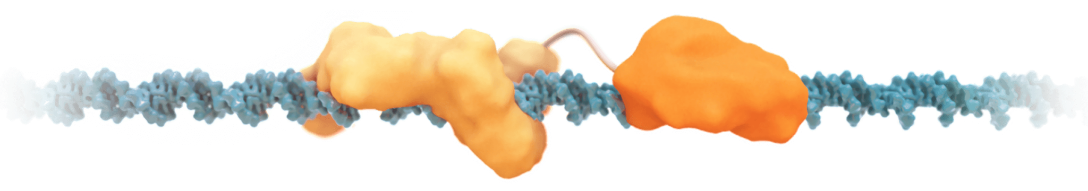
Following translation, the proteins enter the cell nucleus and home into the target IGD, where they make the appropriate epigenetic modifications at the specified Epigenomic Zipcode, or EpiZip™. The mRNA and expressed proteins are degraded within a few days by normal cellular processes, while the programmed epigenetic modification(s) can persist for either days, weeks, or months, depending on the duration engineered into the epigenomic controller by virtue of the target and effector domains. Since this approach preserves native nucleic acid sequences, it may eliminate the safety concerns associated with other treatment modalities that modify the genome.
Benefits of Epigenomic Controllers
Specificity
The DNA-binding domain expressed by the epigenomic controller is highly specific and can be engineered to target and bind to a single EpiZip comprised of a unique ~20 nucleotide sequence.
Tunability
Epigenomic controllers are designed to harness the full spectrum of epigenetic mechanisms, such as DNA methylation/demethylation and those controlling the state of chromatin (e.g., histone modification, acetylation, etc.). Acting at different types of regulatory elements in an IGD, including CTCF regions, enhancers, silencers, and promoters, epigenomic controllers are engineered to tune and restore gene expression to normal levels rather than an “all on” or “all off” binary fashion.
Durability
An epigenomic controller's therapeutic response can be tailored to potentially last days, weeks, or months, offering the opportunity to optimize treatment regimens for efficacy and safety and allow for broad flexibility in dosing intervals. Epigenomic controllers are designed to be short-lived in the target tissues while the epigenetic modifications and their effects on gene expression are durable. This may circumvent safety concerns associated with prolonged exposure to a therapeutic drug substance.
Our epigenomic controllers have the potential to transform medicine by delivering on the promise of epigenetics.
